Quebec is more than just a province; it is a massive, geographic wonder that bridges the gap between old-world European charm and the rugged wilderness of North America.
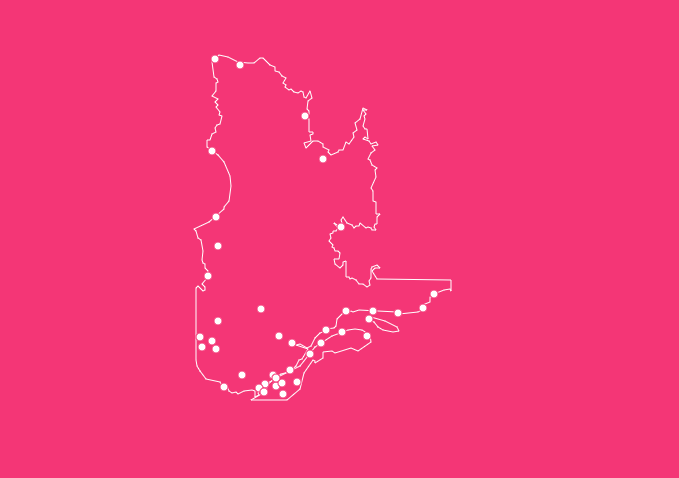
As Canada’s largest province by area, it covers a staggering 1.5 million square kilometers making it roughly three times the size of France or Texas.
Understanding the map of Quebec with cities is essential for students, travelers, and researchers alike.
Interactive Map Tool: How to Use Features on This Page
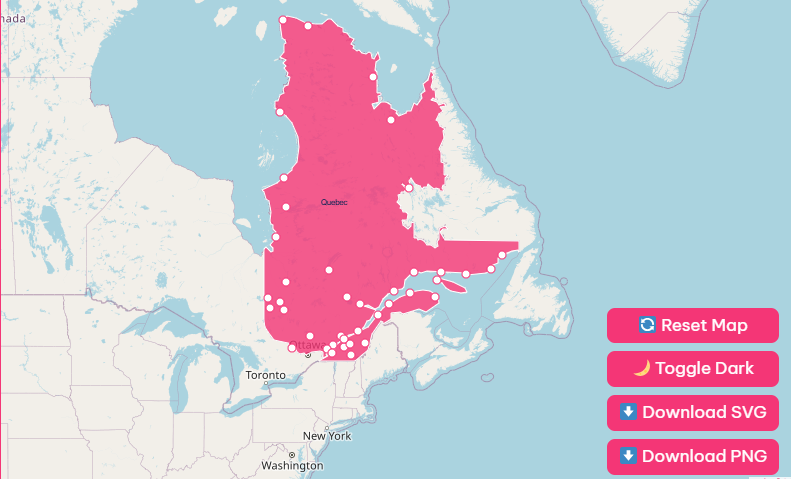
Hover and Highlight Functionality
When you move your cursor over specific regions or city dots on the map, a dialogue box will appear.
Zoom and Pan Controls
Quebec is massive. To see the intricate details of the road networks around Laval or Longueuil, use the + and – buttons located in the bottom right corner of the map viewer.
Reset and Dark Mode
Gotten too lost in the northern wilderness? Simply hit the “Reset” button to return the map to its default, province-wide view.
Download Options: Printable Maps for Every Need
Blank Printable SVG
Ideal for geography quizzes or coloring assignments. This vector file allows you to print the map at any size without losing quality.
High-Detail PNG
This version includes all major highways, city labels, regional borders, and topographical shading. It is perfect for trip planning or detailed reference.
Quebec at a Glance: Geographical and Historical Overview
To truly understand the map, you must understand the land itself. Quebec is a land of contrasts, where ancient rock meets fertile valleys.
Important Quebec Insights
| Feature | Data |
| Capital City | Quebec City |
| Largest City | Montreal |
| Total Area | ~1,667,441 km² |
| Population | ~9,000,000 (Estimate) |
| Official Language | French |
| Highest Point | Mont D’Iberville (1,652m) |
| Motto | Je me souviens (I remember) |
Historical Context
The map of Quebec has changed significantly over centuries. Long before European settlers arrived, the land was inhabited by Indigenous peoples, including the Cree, Innu, and Algonquin nations.
The arrival of Samuel de Champlain in 1608 marked the founding of Quebec City and the beginning of New France.
Geographically, settlement patterns were dictated by the waterways.
The St. Lawrence River was the original “highway” of the province, which is why the vast majority of cities on the map are located along its banks.
Even today, despite the province’s massive size, the northern regions remain sparsely populated, echoing the historical trend of settling where the water flows.
The Three Great Geographic Regions
When analyzing a physical map of Quebec, you will notice three distinct landforms that dictate the climate, economy, and population density of the province.
1. The St. Lawrence Lowlands
This is the heartland of Quebec. Though it is the smallest of the three regions, it is home to the majority of the population.
- Location: Runs along the St. Lawrence River.
- Features: Flat, fertile plains and sedimentary rock.
- Importance: This is the agricultural and industrial engine of the province. Cities like Montreal, Quebec City, and Gatineau are located here.
2. The Canadian Shield
Covering nearly 90% of Quebec, the Canadian Shield is a massive, rocky plateau.
- Location: Covers the entire northern and central portion of the province.
- Features: Ancient igneous rock, dense boreal forests, and hundreds of thousands of lakes.
- Importance: While sparsely populated, this region is crucial for mining (gold, iron, copper) and hydroelectricity generation.
3. The Appalachian Region
If you look at the southeastern part of the map, you will see rolling mountains and jagged coastlines.
- Location: South of the St. Lawrence River, bordering the United States and New Brunswick.
- Features: Eroded mountain ranges and plateaus.
- Importance: This area is famous for tourism, forestry, and mining (notably asbestos in the past). It includes the picturesque Gaspé Peninsula.
Major Cities of Quebec
Quebec’s urban landscape is a blend of modern metropolises and historic fortified towns. Here is a breakdown of the major urban centers you will find on the map.
Montreal
Montreal is not just the largest city in Quebec; it is the second-largest French-speaking city in the world after Paris.
Located on an island in the St. Lawrence River, it serves as a major hub for commerce, aerospace, culture, and technology. It is vibrant, multicultural, and historically significant.
Quebec City
As the provincial capital, Quebec City is the soul of the province. It is the only fortified city in North America north of Mexico, with its historic district (Old Quebec) designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
On the map, you will find it sitting atop Cap Diamant, overlooking the narrowing of the river.
Gatineau
Located directly across the Ottawa River from Canada’s capital, Ottawa, Gatineau is a key urban center in western Quebec. It houses many government offices and serves as a gateway to the beautiful Gatineau Park.
List of Famous Quebec Cities
| City | Region | Known For |
| Montreal | St. Lawrence Lowlands | Festivals, History, Cuisine |
| Quebec City | Capitale-Nationale | Fortifications, Government |
| Laval | Greater Montreal | Suburbs, Shopping, biotech |
| Gatineau | Outaouais | Museum of History, Government |
| Sherbrooke | Estrie (Eastern Townships) | University, Nature |
| Trois-Rivières | Mauricie | Pulp and paper history |
| Saguenay | Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean | Aluminum, Fjord du Saguenay |
Borders and Neighboring Regions
Quebec does not exist in isolation. Its borders are expansive and connect it to various distinct economic zones.
West
It shares a long border with Ontario, defined largely by the Ottawa River, and bounded by Hudson Bay and James Bay to the northwest.
East
It borders the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The border here stretches through the remote wilderness of the Canadian Shield.
South
Quebec shares an international border with four US states: New York, Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine. It also borders the Canadian province of New Brunswick.
North
The northern tip extends to the Hudson Strait and Ungava Bay, bordering the territory of Nunavut.
Key Geographical Features: Lakes and Rivers
You cannot look at a map of Quebec without noticing the blue. Quebec possesses 3% of the world’s renewable fresh water.
The St. Lawrence River
This is the defining feature of the map. Stretching over 1,197 km within Quebec, it connects the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean.
It is responsible for the settlement of the province and remains a vital shipping lane.
The Hydro Network
The province is dotted with massive reservoirs, particularly in the James Bay area.
These man-made and natural bodies of water power the massive hydroelectric dams that allow Quebec to produce clean energy for itself and its neighbors.
Mont D’Iberville
For those looking for elevation on the map, look to the Torngat Mountains in the north.
Mont D’Iberville stands as the highest peak in the province at 1,652 meters, offering a rugged challenge for mountaineers.
Cultural Significance and Regional Identity
Geography shapes culture, and nowhere is this truer than in Quebec. The isolation provided by the Appalachian mountains created unique dialects in the Beauce region.
The maritime geography of the Gaspé Peninsula created a culture centered on fishing and the sea.
The map of Quebec is also a linguistic map.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are 10 common questions regarding the geography and map of Quebec.
Is Quebec bigger than Texas?
Yes. Quebec is roughly 1.5 million square kilometers, while Texas is approximately 695,000 square kilometers. You could fit Texas inside Quebec more than twice.
What is the capital city of Quebec?
The capital city is Quebec City (Ville de Québec), located roughly 250 km northeast of Montreal.
Does the map of Quebec include many islands?
Yes, Quebec includes thousands of islands. The most famous include the Island of Montreal, Île d’Orléans near Quebec City, and Anticosti Island in the Gulf of St. Lawrence.
What is the “Canadian Shield” shown on the map?
It is a massive geologic shield covered by a thin layer of soil. It is rich in minerals and fresh water but is difficult to farm, which is why most people live south of it.
How much of Quebec is covered by forest?
Forests cover more than half of Quebec’s territory, making the forestry industry a vital part of the economy.
Which US states touch the map of Quebec?
Quebec shares a border with Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York.
Where is the highest population density on the map?
The highest density is found in the Greater Montreal Area and along the St. Lawrence River corridor.
Are there English-speaking cities on the map of Quebec?
While French is the official language, many municipalities, especially in western Montreal (like Westmount or Pointe-Claire) and parts of the Outaouais, have large English-speaking populations.
What is the Gaspé Peninsula?
It is a large peninsula in eastern Quebec that extends into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, known for the famous Percé Rock.
Can I drive to the northernmost point of Quebec?
No. The road network ends roughly in the middle of the province. The northern villages in Nunavik are accessible only by plane or boat during the summer.
Explore Quebec Today
If you are planning a visit or simply studying this fascinating province, use the tools and downloads provided in this guide to deepen your understanding.
Ready to see it for yourself? Download our high-resolution map today and start planning your Quebec adventure.